A Colorado forest impacted by a mountain pine beetle outbreak. Notice the dead trees mixed with live trees. Forests like this with dead trees from mountain pine beetle outbreaks cover millions of acres across western North America.
The activities are as follows:
- Teacher Guide
- Student activity, Graph Type A, Level 2
- Student activity, Graph Type B, Level 2
- Student activity, Graph Type C, Level 2
- Grading Rubric
A beetle the size of a grain of rice seems insignificant compared to a vast forest. However, during outbreaks the number of mountain pine beetles can skyrocket, leading to the death of many trees. The beetles bore their way through tree bark and introduce blue stain fungi. The blue stain fungi kills the tree by blocking water movement. Recent outbreaks of mountain pine beetles killed millions of acres of lodgepole pine trees across western North America. Widespread tree death caused by mountain pine beetles can impact human safety, wildfires, nearby streamflow, and habitat for wildlife.
Mountain pine beetles are native to western North America and outbreak cycles are a natural process in these forests. However, the climate and forest conditions have been more favorable for mountain pine beetles during recent outbreaks than in the past. These conditions caused more severe outbreaks than those seen before.

Logs from mountain pine beetle killed lodgepole pine trees. The blue stain fungi is visible around the edge of each log. Mountain pine beetles introduce this fungus to the tree.
When Tony moved to Colorado, he drove through the mountains eager to see beautiful forests. The forest he saw was not the green forest he expected. Many of the trees were dead! Upon closer examination he realized that some forests had fewer dead trees than others. This caused him to wonder why certain areas were greatly impacted by the mountain pine beetles while others had fewer dead trees. Tony later got a job as a field technician for Colorado State University. During this job he measured trees in mountain forests. He carefully observed the forest and looked for patterns of where trees seemed to be dead and where they were alive.
Tony thought that the size of the trees in the forest might be related to whether they were attacked and killed by beetles. A larger tree might be easier for a beetle to find and might be a better source of food.To test this idea, Tony and a team of scientists visited many forests in northern Colorado. At each site they recorded the diameter of each tree’s trunk, which is a measure of the size of the tree. They also recorded the tree species and whether it was alive or dead. They then used these values to calculate the average tree size and the percent of trees killed for each site.
Featured scientist: Tony Vorster from Colorado State University
Flesch–Kincaid Reading Grade Level = 8.3
There is one scientific paper associated with the data in this Data Nugget. The citation and PDF of the paper is below:
- Vorster, A.G., Evangelista, P.H., Stohlgren, T.J., Kumar, S., Rhoades, C.C., Hubbard, R.M., Cheng, A.S., & Elder, K. (2017). Severity of a mountain pine beetle outbreak across a range of stand conditions in Fraser Experimental Forest, Colorado, United States. Forest Ecology and Management 389:116-126.
Students can complete this Data Nugget along with Tony! In this video, Tony provides more background on how he became interested in doing research, how he collects his data, and details on how to construct graphs.
















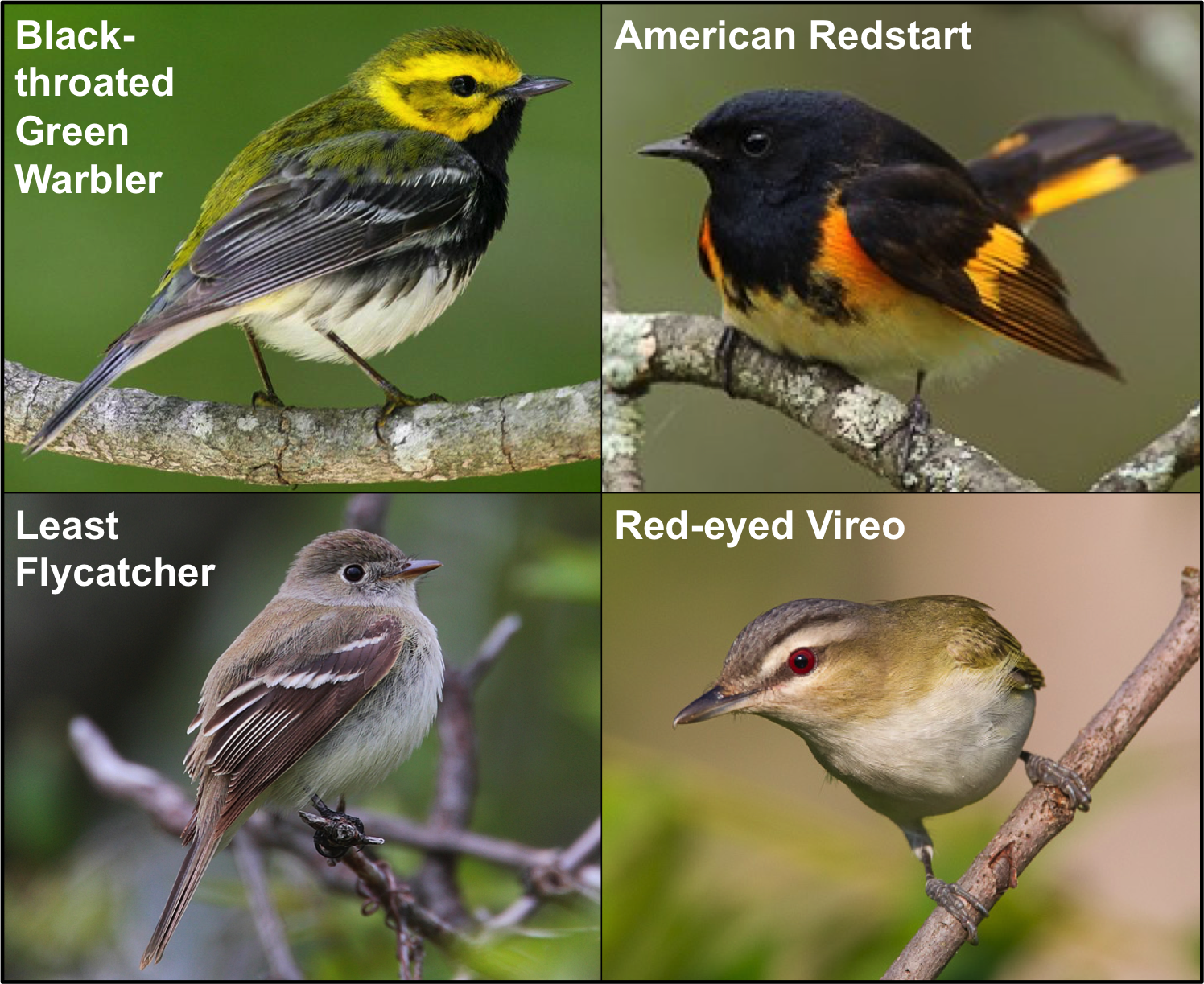
 About Carrie: I have been interested in animal behavior and behavioral ecology since my second year in college at the University of Tennessee. I am primarily interested in how variation in ecology and environment affect communication and signaling in birds. I have also studied various types of memory and am interested in how animals learn and use information depending on how their environment varies over space and time. I am currently working on my PhD in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation Biology at the University of Nevada Reno and once I finish I hope to become a professor at a university so that I can continue to conduct research and teach students about animal behavior. In my spare time I love hiking with my friends and dogs, and watching comedies!
About Carrie: I have been interested in animal behavior and behavioral ecology since my second year in college at the University of Tennessee. I am primarily interested in how variation in ecology and environment affect communication and signaling in birds. I have also studied various types of memory and am interested in how animals learn and use information depending on how their environment varies over space and time. I am currently working on my PhD in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation Biology at the University of Nevada Reno and once I finish I hope to become a professor at a university so that I can continue to conduct research and teach students about animal behavior. In my spare time I love hiking with my friends and dogs, and watching comedies!