
Cayo Santiago rhesus macaques. Photo by Raisa Hernández Pacheco.
The activities are as follows:
- Teacher Guide
- Student activity, Graph Type A, Level 3
- Student activity, Graph Type B, Level 3
- Student activity, Graph Type C, Level 3
- PowerPoint of images
- Scientist Profile on Project Biodiversify
- Scientist Profile
- Grading Rubric
- Digital Data Nugget on DataClassroom
It is easy to identify a deer as male when you see his huge antlers, or a peacock as male by his stunning set of colorful tail feathers. But you may wonder, how do these traits come about, and why don’t both males and females have them? These extravagant traits are thought to be the result of sexual selection. This process happens when females mate with males that they think have the sexiest traits. These traits get passed on to future male offspring, leading to a change in the selected traits over time. Because females are only choosing these traits in males, sexual selection often leads to sexual dimorphism between males and females. This means that the sexes do not look the same. Often males will be larger and have more elaborate traits than females.

Craniums of an adult male (left) and an adult female (right) rhesus macaque. Photo by Raisa Hernández Pacheco and Damián A. Concepción Pérez.
One species that shows strong sexual dimorphism is rhesus macaques. In this species of monkey, males are much larger than females. Cayo Santiago is a small island off the shore of Puerto Rico. On this island lives one of the oldest free-ranging rhesus macaque colonies in the world. This population has no predators and food is plentiful. Scientists at Cayo Santiago have gathered data on these monkeys and their habitat for over 70 years. Every year when new monkeys are born they are captured, marked with a unique tattoo ID, and released. This program allows scientists to monitor individual monkeys over their entire lives and record the sex, date of birth, and date of death. Once a monkey dies and its body is recovered in the field, skeletal specimens are stored in a museum for further research.
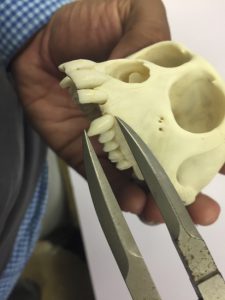
Damián measuring canine length in a rhesus macaque skeletal specimen. Photo by Raisa Hernández Pacheco.
These skeletal specimens can be used by scientists today to ask new and exciting questions. Raisa and Damián are both interested in studying sexual dimorphism in rhesus macaques. They want to find out what causes the differences between the sexes. They chose to focus on the length of the very large canine teeth in male and female macaques. They expected that canine teeth may be under sexual selection in males for two reasons. First, rhesus macaques are mostly vegetarians, so they don’t need long canines for the same purpose as other meat-eating species that use them to catch prey. Second, male rhesus macaques often bare their teeth at other males when they are competing for mates. Females could see the long canines as a sign of good genes and may prefer to mate with that trait. Excited by these ideas, Raisa and Damián set out to investigate the museum’s skeletal specimens to check whether there is sexual dimorphism in canine length. This is the first step in collecting evidence to see whether male canines are under sexual selection by females.
They measured canine length of four male and four female rhesus skeletal specimens dating back to the 1970s. Measurements were only taken from individuals that died as adults to make sure canines were fully developed and that differences in length could not be attributed to age. Raisa and Damián predicted that males would have significantly longer canines compared to those of females. If so, this would be the first step to determine whether sexual selection was operating in the population.
Featured scientists: Raisa Hernández-Pacheco from University of Richmond and Damián A. Concepción Pérez from Wilder Middle School. Research conducted at the Laboratory of Primate Morphology at the University of Puerto Rico Medical Sciences Campus. Skeletal specimens came from the population of rhesus macaques on Cayo Santiago.
Flesch–Kincaid Reading Grade Level = 9.8
Damián and Raisa created a teaching module, called Unknown Bones. It is an inquiry-based educational activity for high school students in which they apply data analysis and statistics to understand sexual selection and illustrate sexual dimorphism in Cayo Santiago rhesus macaques.
 About Raisa: I am interested in understanding the drivers shaping population dynamics, and have dedicated my studies to modeling the effects of biotic and abiotic factors on populations of invertebrates and vertebrates. In 2013, I obtained my PhD from the University of Puerto Rico after assessing the effects of mass bleaching on Caribbean coral populations. Right after, I joined the Caribbean Primate Research Center and the Max-Planck Odense Center to study the long-term dynamics of the Cayo Santiago rhesus macaque population. At the Grayson lab, I am studying the population of red-backed salamanders in Richmond; its density, spatial arrangement, and space use.
About Raisa: I am interested in understanding the drivers shaping population dynamics, and have dedicated my studies to modeling the effects of biotic and abiotic factors on populations of invertebrates and vertebrates. In 2013, I obtained my PhD from the University of Puerto Rico after assessing the effects of mass bleaching on Caribbean coral populations. Right after, I joined the Caribbean Primate Research Center and the Max-Planck Odense Center to study the long-term dynamics of the Cayo Santiago rhesus macaque population. At the Grayson lab, I am studying the population of red-backed salamanders in Richmond; its density, spatial arrangement, and space use.
 About Damián: I am a middle and high school Science and Math teacher. I have always been searching for innovative ways to get my students engaged in the science classroom and to connect their new knowledge with the real-world. In thinking of ways to help my students learn, I engaged my self with the scientific community collaborating in scientific projects and creating hands-on, interactive, and inspiring teaching lessons. It is my main interest to develop ideas that could positively contribute to any student’s STEM education.
About Damián: I am a middle and high school Science and Math teacher. I have always been searching for innovative ways to get my students engaged in the science classroom and to connect their new knowledge with the real-world. In thinking of ways to help my students learn, I engaged my self with the scientific community collaborating in scientific projects and creating hands-on, interactive, and inspiring teaching lessons. It is my main interest to develop ideas that could positively contribute to any student’s STEM education.
