In Part 1, you examined the effects of genetics and environment on anal fin color in male bluefin killifish. The data from Becky’s experiment showed that both genetics and environment work together to determine whether male offspring had blue, yellow, or red anal fins. You will now examine how the father’s genetics, specifically their fin color pattern, affects anal fin color in their sons. When we factor in the genetics of the father, and not just the population he came from, does this influence our interpretation of the data?

The color polymorphism in bluefin killifish – males display anal fins in blue, red, or yellow.
The activities are as follows:
- Teacher Guide
- Student activity, Graph Type A, Level 4
- Student activity, Graph Type B, Level 4
- Student activity, Graph Type C, Level 4
- Grading Rubric
For her experiment, Becky collected male and female fish from both a swamp (26 Mile Bend) and a spring (Wakulla) population. Most of the males in the swamp have blue anal fins, but some have red or yellow. Most of the males from the spring have red or yellow anal fins, but some have blue. Becky decided to add data about the father’s fin color pattern into her existing analysis from Part 1 to see how it affected her interpretation of the results.
In Part 1, Becky was looking at the genetics from the population level. Looking at the data this way, we saw parents from the 26 Mile Bend swamp population were more likely to have sons with blue anal fins than parents from the Wakulla spring. Parents from the 26 Mile Bend were also much more likely to have sons with higher levels of plasticity, meaning they responded more to the environment they were raised in. This means there was a big difference between the proportion sons with blue anal fins in the clear and brown water treatments.
Bringing in the color pattern of the fathers now allows Becky to look at the genetics from both the population and the individual level. From both the swamp and spring population, Becky collected males of all colors. Becky measured the color pattern of the fathers and recorded the color of their anal fins and the rear part of their dorsal fins. She used males that were red on the rear portion of the dorsal fin with a blue anal fin (rb), males that were red on both fins (rr), males that were yellow on both fins (yy), and males that were yellow on the rear portion of the dorsal fin with blue a blue anal fin (yb).
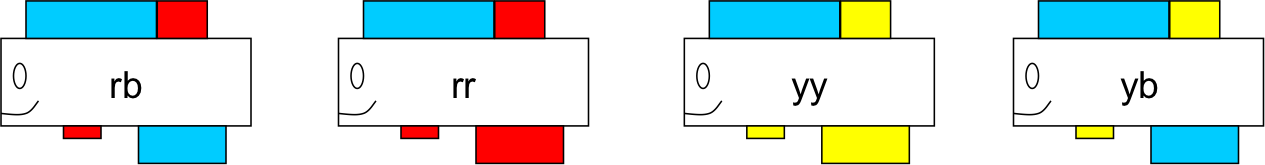
She randomly assigned each father’s sons into one of the water treatments, either clear or brown water. Once the sons developed their fin colors, she recorded the anal fin color. This experimental design allowed her to test whether sons responded differently to the treatment depending on the genetics of their father. She thought that the anal fin color of the sons would be inherited genetically from the father, but would also respond plastically to the environment they were raised in. She predicted fathers with blue anal fins would be more likely to have sons with blue anal fins, especially if they were raised in the brown water treatment. She also predicted that fathers with red and yellow anal fins could have sons with blue anal fins if they were raised in the brown water treatment, but not as many as the blue fathers.
Featured scientist: Becky Fuller from The University of Illinois
Flesch–Kincaid Reading Grade Level = 10.9
About Becky: I consider myself to be an evolutionary biologist who studies fishes. I grew up in a small town riding horses in 4-H and working in a veterinary clinic. As an undergraduate at the University of Nebraska at Lincoln, I was interested in biology and considering either medical or veterinary school. Two things led to me research in ecology and evolution. In the summer of 1991, I was taking courses at Cedar Point Biological Field Station which was run by the University of Nebraska. I met Dr. Anthony Joern (Tony) who was studying grasshopper community ecology. Tony hired me onto his field crew that summer after the courses were finished. I went on to do an undergraduate thesis under Tony’s mentorship where I studied predation on grasshoppers. I caught the “science bug” and never looked back. Following my undergraduate work, I went to Uppsala University in Sweden on a Fulbright Scholarship. Here, I developed my love for fish and aquatics. I worked with Dr. Anders Berglund on pipefish in a fjord on the west coast of Sweden. Since then, I have had many wonderful advisers, instructors, mentors, and collaborators who have helped me develop skills along the numerous fronts required for a successful career in science. I consider myself very fortunate to have a job where I can do science and teach young, enthusiastic undergraduates.


Hi!
There doesn’t seem to be a live link for the student activities. Is there a chance those will be available in early January?
This looks great!
Thanks!